Role of Humankind in Antibiotic, Antimicrobial- Drug Resistance of Microorganisms- Juniper Publishers
Juniper Publishers- Journal of Cell Science
Opinion
Overuse of antibiotics, antimicrobial-drugs by human
and animals, leading to complete loss of important and helpful microbes
and enhancing the grown and increasing the harmful microbe population.
Every living thing tries to survive in every environment, even in
stressful conditions by adopting the surrounding conditions and sustain
the harsh environment. Without knowing we are providing the
microorganisms the conditions which increase the capability to wash out
the complete human population. Microorganisms are the vast populated
living organisms, many are useful for protecting the immune system from
infections and some are harmful too. By the discovery of penicillin by
Sir Alexander Fleming in 1928 [1,2] started a modern era of antibiotics.
Penicillin saved millions of lives during world war-II [1].
Thereafter, major growth took place in the antibiotic
discovery that played a key role in modern medicine. Until the first
case of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is identified
in 1962 [1,3]. After this the effectiveness
of antibiotics decreases suddenly, resistance has eventually observed
for almost all antibiotics that have been developed [3]. Even though
vancomycin was introduced for curing MRSA in clinical practices,
unfortunately, bacteria developed resistance to this antibiotic to [1].
We are responsible for the antibiotic resistance by overuse of
antibiotics and drugs. Bacteria are getting evolved because of
antibiotic overuse, which increases the resistivity towards the
antibiotics and drugs [4,5]. Where the inheritance takes place in the
bacteria that passes to the next generation. Spontaneous mutations can
also help in developing resistance. Through natural selection, the
bacteria reproduce the resistance offspring because of losing drug
sensitivity by antibiotics [3,6]. Not only within itself have bacteria
also had the ability to transfer resistance to other bacteria through
horizontal gene transfer (HGT) [6]. Subinhibitory and subtherapeutic
antibiotic concentrations can promote the development of antibiotic
resistance by supporting genetic alterations, such as changes in gene
expression, HGT, and mutagenesis (Figure 1).
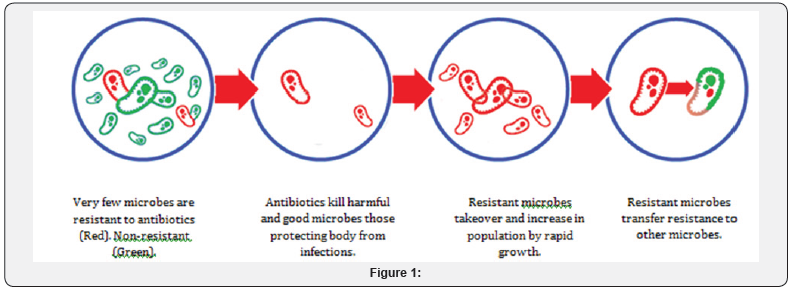
We are neglecting the antibiotic and antimicrobial
drugs overuse alarm [6]. Now a day’s commercial company advertising many
different kinds of antibiotics, drugs, and disinfectants promising they
can kill the germs and that increase the immunity. We are completely
losing our resistance and immunity towards harmful germs. Exposing to
fewer germs is also very important part of immunizing our own system
this is also known as acquired immunity. This type of immunity
stimulates the immune system readily with the memory cells those can
protect our system in a
future attack by the same microbes.
We use many chemicals, gels, and bars to kill the
microorganisms, but we are forgetting that we are creating
a stressful environment for the microorganisms which force
them to evolve for the survival. Here comes the problem once
the microorganisms start evolving, nothing can stop them. If we
think of a new drug to kill them, they again build up resistance
power against the new drug (Figure 2). Using more antibiotics,
drugs, and chemicals to kill germs may also completely wash out
the useful microbes which help in protecting our immune system
and helps in the digestion process. Now the antibiotic/drugresistant
microbes grow faster and spread throughout the body.
And those microbes pass the resistivity to their neighboring
microbes [7-11].

“As our ancestors say prevention is better than cure”





Comments
Post a Comment